What Is a Humidity Sensor?
A humidity sensor is an electronic device that measures the amount of water vapor present in the air or gases. It essentially detects changes in the environment caused by moisture and translates those changes into an electrical signal. This signal can then be used to determine the relative humidity (RH), which is a measure of how much moisture is in the air compared to the maximum amount it can hold at a specific temperature.
There are various types of humidity sensors, each operating on different principles:
- Capacitive: These sensors contain electrodes that store an electrical charge. As humidity levels rise, the water vapor molecules absorb some of the charge, leading to a change in capacitance (the ability to store charge).
- Resistive: These sensors use a material that changes its resistance based on moisture absorption. High humidity increases conductivity, lowering resistance, and vice versa.
- Thermal conductivity: These sensors measure the differing thermal conductivity of dry air and air with water vapor. One sensor may be heated, and the rate at which it cools due to the surrounding air is influenced by humidity.
Here are some common applications of humidity sensors:
- HVAC systems: Regulating temperature and humidity for comfort and energy efficiency.
- Weather monitoring: Tracking humidity levels for weather forecasting.
- Indoor air quality (IAQ) monitoring: Maintaining healthy and comfortable indoor air conditions.
- Agriculture: Optimizing crop growth by controlling humidity in greenhouses.
- Industrial processes: Ensuring consistent product quality in moisture-sensitive manufacturing.
- Consumer electronics: Enhancing features in smartphones, wearables, and other devices that benefit from humidity sensing (e.g., fog detection on camera lenses).
By measuring humidity, these sensors play a crucial role in various applications where moisture control is essential.

Principle of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors function by detecting changes in the environment caused by moisture and translating those changes into an electrical signal. There are three main types of humidity sensors, each utilizing different principles to achieve this:
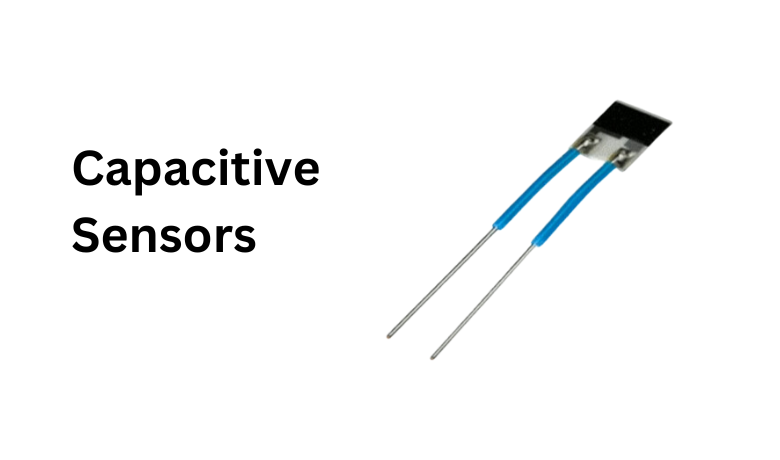
1. Capacitive Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors rely on the property of capacitance, which is the ability of a device to store electrical charge. They consist of two electrodes separated by a thin layer of a hygroscopic material (easily absorbs water vapor).
- Operation: When dry, the hygroscopic material has a low capacitance. As humidity increases, water vapor molecules are absorbed by the material, causing a change in its dielectric constant (ability to store electrical charge) and increasing the overall capacitance between the electrodes.
- Measurement: By measuring the change in capacitance, the sensor can determine the relative humidity level.
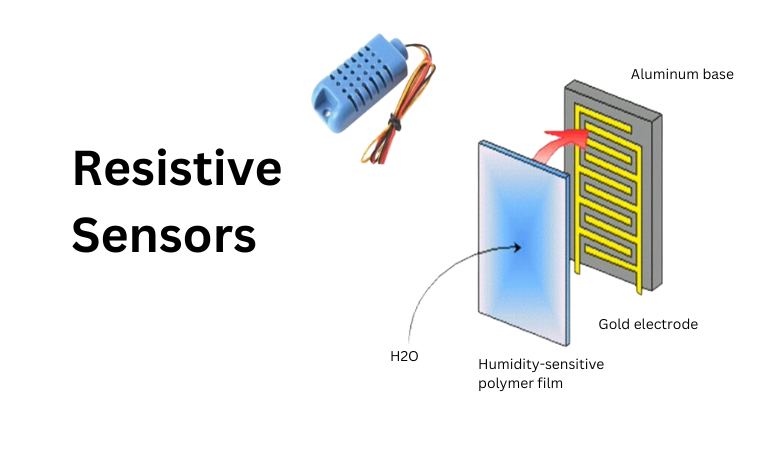
2. Resistive Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors utilize a hygroscopic material that changes its electrical resistance based on the amount of absorbed water vapor.
- Operation: The resistive material is typically a polymer film or a salt solution sandwiched between two electrodes. When dry, the material has a high resistance. As humidity increases, water vapor is absorbed, causing the material to swell and its ions to become more mobile. This increases the conductivity and lowers the resistance between the electrodes.
- Measurement: The sensor measures the change in resistance, which can be correlated to the relative humidity level.
3. Thermal Conductivity Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors exploit the difference in thermal conductivity between dry air and air containing water vapor.
- Operation: There are two main designs:
- Wet-bulb/dry-bulb: This type uses two sensors, one with a wick constantly wetted (wet-bulb) and the other dry (dry-bulb). The difference in cooling rates between the sensors due to the varying thermal conductivity of moist vs. dry air is used to calculate humidity.
- Heated: This type uses a single heated sensor. The rate at which the heated sensor cools down is influenced by the thermal conductivity of the surrounding air, which is affected by humidity. Higher humidity leads to faster cooling due to increased water vapor conductivity.
- Measurement: By measuring the temperature difference or cooling rate, the sensor can determine the relative humidity.
Additional Considerations:
- Calibration: Humidity sensors may require periodic calibration to maintain accuracy, especially in environments with frequent humidity fluctuations.
- Response Time: The time it takes for the sensor to react to changes in humidity can vary depending on the type and design.
These principles provide the foundation for how humidity sensors function, allowing them to play a vital role in various applications where moisture control is critical.
Types of Humidity Sensors
Humidity sensors come in various forms, each employing distinct principles to measure the amount of water vapor in the air. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
1. Capacitive Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors rely on capacitance, the ability of a device to store electrical charge. They consist of two electrodes separated by a hygroscopic material (easily absorbs water vapor).
- Working: When dry, the hygroscopic material has a low capacitance. As humidity rises, water vapor molecules are absorbed, causing a change in its dielectric constant (ability to store charge) and increasing the overall capacitance between the electrodes.
- Measurement: By measuring the change in capacitance, the sensor can determine the relative humidity level.
- Advantages: Capacitive sensors offer high accuracy, excellent stability, and a wide operating range. They are also compact and have a fast response time.
- Disadvantages: They can be more expensive than some other types and may be slightly more susceptible to contamination.
2. Resistive Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors utilize a hygroscopic material that changes its electrical resistance based on the amount of absorbed water vapor.
- Working: The resistive material is typically a polymer film or a salt solution sandwiched between two electrodes. When dry, the material has a high resistance. As humidity increases, water vapor is absorbed, causing the material to swell and its ions to become more mobile. This increases the conductivity and lowers the resistance between the electrodes.
- Measurement: The sensor measures the change in resistance, which can be correlated to the relative humidity level.
- Advantages: Resistive sensors are generally inexpensive and offer a simple design.
- Disadvantages: They can be less accurate and less stable than capacitive sensors. They may also have slower response times and be more prone to drift over time.
3. Thermal Conductivity Sensors:
- Principle: These sensors exploit the difference in thermal conductivity between dry air and air containing water vapor.
- Working: There are two main designs:
- Wet-bulb/dry-bulb: This type uses two sensors, one with a wick constantly wetted (wet-bulb) and the other dry (dry-bulb). The difference in cooling rates between the sensors due to the varying thermal conductivity of moist vs. dry air is used to calculate humidity.
- Heated: This type uses a single heated sensor. The rate at which the heated sensor cools down is influenced by the thermal conductivity of the surrounding air, which is affected by humidity. Higher humidity leads to faster cooling due to increased water vapor conductivity.
- Measurement: By measuring the temperature difference or cooling rate, the sensor can determine the relative humidity.
- Advantages: Thermal conductivity sensors can be used in harsh environments and are relatively resistant to contamination.
- Disadvantages: They can be less accurate than other types, especially at lower humidity levels. They may also be slower to respond to changes in humidity and have higher power consumption.

Additional Types:
- Gravimetric Sensors: These highly accurate sensors directly measure the weight of water vapor absorbed by a desiccant (drying agent). However, they are bulky, complex, and not suitable for most applications.
- Electrolytic Sensors: These sensors use an electrolyte solution that conducts electricity based on the amount of absorbed water vapor. They offer good accuracy but require regular maintenance and are not ideal for high-humidity environments.
- Optical Sensors: Newer technologies are emerging that utilize optical properties to detect humidity. These sensors can be very sensitive and may offer advantages in specific applications.
Choosing the Right Sensor:
The most suitable humidity sensor for your project depends on various factors, including:
- Required Accuracy: How critical is precise humidity measurement?
- Operating Range: What range of humidity levels will the sensor be exposed to?
- Response Time: How quickly does the sensor need to react to changes in humidity?
- Environmental Conditions: Will the sensor be used in a harsh environment?
- Cost and Power Consumption: What are your budget and power constraints?
By considering these factors and the unique characteristics of each type, you can select the optimal humidity sensor for your specific needs.
Here, we List Top 10 humidity sensor Manufacturer in the Market, you can check details, choose right humidity sensor supplier.
Sensirion
Manufacturer Overview
A renowned Swiss high-tech company, Sensirion is a world leader in sensor manufacturing focusing on high-performance, low-power, and digital output humidity and differential pressure sensors.
They are known for their innovative CMOSens® technology which integrates the sensor element, signal processing, and calibration data on a single chip.
Honeywell
Manufacturer Overview
* Website United States, North Carolina
* Address: 855 S. Mint Street, Charlotte, North Carolina, United States of America
A global technology giant, Honeywell’s Sensing and Control division offers a vast portfolio of sensors, including humidity sensors.
They provide various types of temperature and humidity sensors, including digital, voltage, and capacitance output options.
Bosch Sensortec
Manufacturer Overview
A leading supplier of microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensors, Bosch Sensortec offers a wide range of environmental sensors, including humidity sensors. Their products are known for their small size, low power consumption, and high accuracy.
Texas Instruments
Manufacturer Overview
A well-established semiconductor company, Texas Instruments offers various humidity sensor options, including integrated circuits and standalone sensors.
Their products cater to a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial automation.
NXP Semiconductors
Manufacturer Overview
Another major player in the semiconductor industry, NXP offers humidity sensors with a focus on low power consumption and high reliability.
Their products are suitable for various applications, including building automation, HVAC systems, and white goods.
TE Connectivity (TE)
Manufacturer Overview
TE Connectivity (TE) is a leading manufacturer of connectors and other electronic components. They also offer a range of humidity sensors, including capacitive and resistive types.
Their sensors are known for their durability and long-term stability.
STMicroelectronics
Manufacturer Overview
A global provider of semiconductor devices, STMicroelectronics offers various humidity sensor solutions, including digital and analog options.
Their products are known for their compact size and integration capabilities.
Amphenol
Manufacturer Overview
A leading manufacturer of interconnect products, Amphenol also offers a range of environmental sensors, including humidity sensors.
Their sensors are known for their robustness and suitability for harsh environments.
Laird
Manufacturer Overview
Specializing in wireless connectivity and smart technologies, Laird also offers various humidity sensor solutions.
Their sensors are often integrated with other sensing technologies to provide comprehensive environmental monitoring.
MEAS (Measurement Specialties)
Manufacturer Overview
(Measurement Specialties): A leading provider of performance-critical sensors and sensor-based solutions, MEAS offers a comprehensive line of humidity sensors.
Their products cater to various applications, including automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.
Main Features
Some key features of each humidity sensor product, hope thesee information is helpful for your choose :
| Manufacturers | Business Focus | Main Products | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensirion | High-performance, low-power sensors | SHT series, CMOSens® technology | – Excellent accuracy & reliability – Low power consumption – Compact, digital package – Integrated temperature & humidity sensing (SHT series) – CMOSens® technology for on-chip sensor element, signal processing, and calibration |
| Honeywell | Vast sensor portfolio | HIH series | – High performance & reliability – Diverse output options (digital, voltage, capacitance) – Suitable for demanding applications (building automation, HVAC, industrial) |
| Bosch Sensortec | MEMS sensors | BME280 | – Integrated temperature, humidity, & barometric pressure sensing – Compact & versatile – Ideal for weather monitoring, wearables, air quality |
| Texas Instruments | Semiconductors | HDC2010 | – Low power consumption – High accuracy – Well-suited for battery-powered applications |
| NXP Semiconductors | Semiconductors | HTS221 | – Compact & reliable – Low power consumption – Suitable for building automation, white goods, data loggers |
| TE Connectivity (TE) | Connectors & electronic components | HTHT-003 | – Durable & long-lasting – High stability – Suitable for harsh environments |
| STMicroelectronics | Semiconductor devices | HTS21 | – Good accuracy & compact size – Digital output – Ideal for wearables, smartphones, building automation |
| Amphenol | Interconnect products | AHT series | – Robust & withstands harsh environments – Various options for diverse applications |
| Laird | Wireless connectivity & smart technologies | RH series | – Integrated temperature sensing – Digital output – Often combined with other Laird products for comprehensive monitoring |
| MEAS (Measurement Specialties) | Performance-critical sensors | HS300x series | – High-performance for demanding applications – Excellent accuracy & stability – Ideal for industrial, medical, and automotive use |
These are just a few of the many humidity sensor manufacturers on the market.
The right sensor for your application will depend on your specific needs, such as accuracy, power consumption, size, and cost.
Consider researching these companies and others to find the best fit for your project.






