
Why Standard Sensors Fail in High-Temperature Humidity Measurement
Humidity measurement is relatively straightforward at ambient conditions. Most standard sensors perform adequately in offices,
From the most remote corners of the Earth comes the fuel that makes modern life possible.
Home » I2C Temperature Humidity Sensor Probe
HENGKO is one of the best suppliers of I2C Temperature Humidity Sensor Probes. Our probes, designed for precision and durability, offer reliable and accurate measurements of both temperature and humidity.
Ideal for various applications, HENGKO’s sensors are highly sought after in industries where environmental monitoring is critical.
Versatile I2C Temperature and Humidity Sensors: A Range of Customizable Probes for Every Need.
I2C Temperature and Humidity Sensor with Different Design Probe, like dual navigation, single navigation, Hex screw, knurled waterproof, heat shrink tube, double knurled, silver edge knurled, small hexagonal navigation and six-star probe
Replacement L-Type Design, I2C Humidity Probe for Temperature and Humidity Transmitter
I2C Long Probe Temperature Humidity Integrated Transmitter is a sophisticated sensing solution designed to deliver precise and reliable measurements of temperature and humidity. This integrated device features a long probe, making it ideal for reaching into narrow or hard-to-access areas while maintaining accuracy and stability in readings.
HENGKO, a proficient supplier of industrial sensor solutions, stands out with its unique designs and exceptional performance. The range of I2C temperature and humidity sensors and transmitters are extensively utilized across various industries.
Application included sectors like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, and environmental monitoring. HENGKO’s products are highly valued for their accuracy, durability, and adaptability, catering to the diverse and demanding needs of these industries.
You can fully customize unique probe design, I2C, I2C signal line, Output, OEM Your Brand etc
Factory Sales, You will get much lower and competitive price due to our extremely cost-effective control.
You will always meet the ever-changing market needs with our keep-upgrading products.
You will get strong marketing support to help you sell products successfully, material supports include: high resolution product images, cool 3d-effect videos, and a LOT more.









Customize Your Unique I2C Sensor Probe for New Temperature and Humidity Sensors or Transmitters with HENGKO Expert OEM Services.
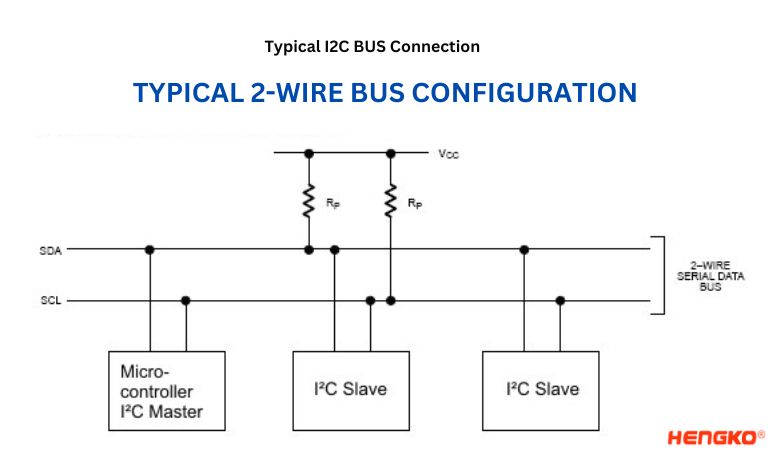
Imagine a bustling city street, but instead of cars and pedestrians, data zips back and forth between buildings. That’s the essence of I2C, a simple yet powerful communication protocol that lets devices talk to each other using just two wires!
An I2C output is essentially the “loudspeaker” of an I2C device. It’s the channel through which it sends data, like sensor readings, control signals, or even entire blocks of information, to other devices on the same I2C bus. Think of it as the data highway exit where information flows out.
Here’s a breakdown of the I2C output:
I2C offers several advantages that make it a popular choice for inter-device communication, especially in embedded systems and robotics:
Overall, I2C outputs provide a versatile and efficient way to connect various devices within a system, making them a cornerstone of modern electronics design.
Anyway, I hope these explanation clarifies the concept of I2C outputs and their role in device communication.
If you have any further questions, feel free to ask!
As Following are some main features of I2C Temperature and Humidity Sensor :
These are just some of the main features and benefits of I2C temperature and humidity sensor and transmitters.
Their ease of use, reliable performance, and versatility make them valuable tools for a wide range of applications.
There are several types of I2C temperature and humidity sensors and transmitters, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here are some of the most common:
The best type of I2C temperature and humidity sensor or transmitter for you will depend on your specific needs, such as:
By considering these factors, you can choose the right type of I2C temperature and humidity sensor or transmitter for your project.
Selecting the perfect I2C temperature and humidity sensor or transmitter can be a bit tricky with so many options available. But fear not, here’s a guide to help you navigate the jungle of sensors and land on the one that’s just right for your project:
Tip: Start with popular and reliable brands like Sensirion, Bosch, Texas Instruments, TE Connectivity for initial exploration.
But, choosing the right I2C temperature and humidity sensor is about balancing your specific requirements with the capabilities and limitations of each type. By carefully considering your needs and researching available options, you’ll be able to find the perfect sensor for your project.
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer to that, as the “best” output for your temperature and humidity sensor or transmitter depends on several factors specific to your application.
So please check some pros and Cons for those 3 kind of output.
Here’s a quick guide based on common use cases:
So, the best output for your temperature and humidity sensor depends on your specific needs and priorities. Consider factors like cable length, data resolution, power consumption, budget, and existing infrastructure to make the most informed decision.
| Feature | 4-20 mA | I2C | RS485 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data format | Analog | Digital | Digital |
| Number of wires | 2 ( we have 4 wires ) | 2 ( we have 4 wires ) | 2 (plus optional ground) ( we have 4 wires ) |
| Transmission distance | Up to hundreds of meters | Up to several meters | Up to several kilometers |
| Noise immunity | High | Moderate | Low |
| Accuracy/Resolution | Moderate | High | High |
| Multiple sensors | No (requires dedicated channels) | Yes (daisy-chaining) | Yes (multi-drop network) |
| Power consumption | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Complexity | Low (existing standard) | Moderate (software interface) | High (termination resistors, cabling) |
| Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
| Ideal for: | Industrial environments, long cable runs | Battery-powered applications, multiple sensors | High data rates, long distances |
some questions about Dew Point and Transmitter and Sensor you and people like to know
A high dew point means that the air can hold a lot of moisture before it becomes saturated and condensation occurs. In general, a dew point above 60°F (15°C) is considered high. High dew points can make the air feel humid and uncomfortable, especially on a hot day.
An I2C temperature and humidity sensor or transmitter is a device that measures both temperature and humidity levels, and then transmits those values digitally to another device using the I2C communication protocol. Here’s a breakdown of its key aspects:
Overall, I2C temperature and humidity sensors or transmitters offer a convenient and efficient way to monitor environmental conditions in various applications. And because ease of use, reliable performance, and versatility make them valuable tools for a wide range of projects.
The I2C protocol, pronounced as “eye-squared-C,” is a simple yet powerful serial communication interface used to connect low-speed peripheral devices to microcontrollers and processors. Let’s break it down:
I2C is a versatile and user-friendly communication protocol that simplifies connecting various devices within a system. Its simplicity, flexibility, and low power consumption make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Absolutely, HENGKO is fully capable of customizing probes according to your specific design or monitoring requirements, especially metal probes for temperature and humidity sensors suited for extremely harsh environments.
So If your project requires such specialized solutions, don’t hesitate to contact HENGKO today.
Contact HENGKO Today for Any Questions for Temperature and Humidity Sensor, Transmitter and Solution

Humidity measurement is relatively straightforward at ambient conditions. Most standard sensors perform adequately in offices,

Industrial drying processes—used in pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, and materials—demand precise control of temperature and humidity.

High-Temperature Humidity Transmitter for 200℃ Industrial Drying Ovens-HG808-T In many manufacturing processes, drying is more

Effective moisture management is essential in facilities where materials, equipment, and processes depend on controlled

In short, Humidity and temperature transmitters measure and send environmental data to control systems. They
Reach out to our expert team for personalized assistance and we’ll promptly provide the best temperature and humidity transmitter and sensor solutions tailored to your specific needs.

Let us tell you why you should choose a dew point transmitter from HENGKO
Answer is simple: HENGKO is Different.

Humidity measurement is relatively straightforward at ambient conditions. Most standard sensors perform adequately in offices, warehouses, and general HVAC environments. However, once temperatures rise above

Humidity measurement is relatively straightforward at ambient conditions. Most standard

Industrial drying processes—used in pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals, and materials—demand precise

High-Temperature Humidity Transmitter for 200℃ Industrial Drying Ovens-HG808-T In many
WhatsApp us